Zhuzhou Weilai New Materials Techonology Co., Ltd
Tel:0731-22160654
Mobile:
+8615773363955(Mr. Duan)
+8615200507438(Ms.Zhang)
E-mail:sales@rheniumcn.com
Fax:0731-22160654
Address:No.103, Building 2, Tiantai
Jingu Industry Park, Tian Yuan
District,Zhuzhou,Hunan,China
There are many types of electrodes used in resistance welding. Today we will deeply explore the resistance welding application and get to know what electrodes will be used.
In this article, we will first introduce resistance welding definition, types of resistance welding, types of resistance welding.
What is resistance welding?
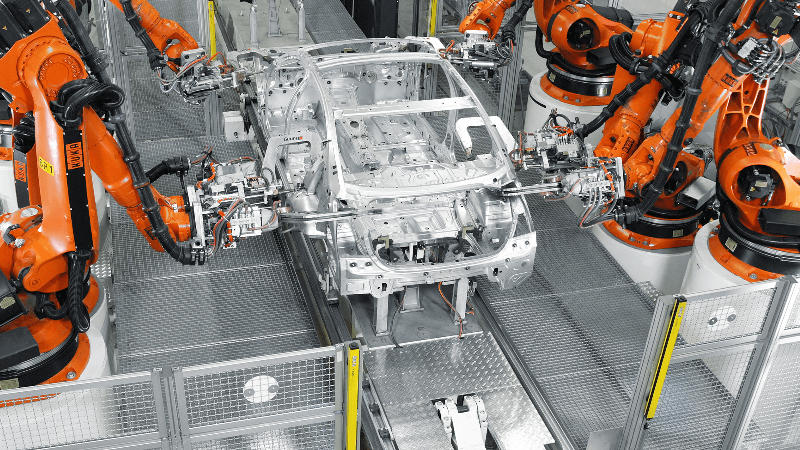
By using resistance welding, the two parts can be connected. They are joined because the parts are under pressure and heated by an electric current until a molten pool form at individual points between them.
It is a cost-effective process without other materials in use and can vary in different forms and be used in different applications.
Advantages of resistance welding:
1. Can achieve automation and be cost-effective
2. Reliable production with a high production rate
3. Little waste or pollution, friendly for the environment
Common Types of Resistance welding?
Based on specific welding applications, there are many resistance welding processes with different uses.
1. Resistance Spot Welding
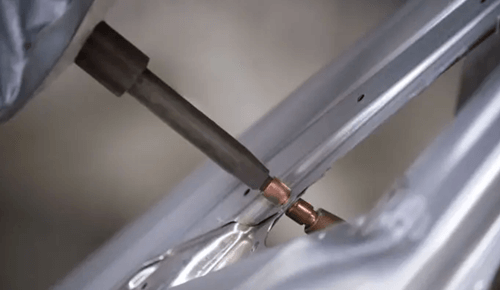
Among resistance welding processes, spot welding is one of the oldest and simplest forms. In spot welding, metal surface points are joined by the heat achieved from resistance to electric current. This process can be used to weld various sheet metal products.
Parameter of spot welding: electrode force, squeeze time, weld or heat time, hold time, and weld current.
Resistance spot welding has been widely used for steel connections in the automotive industry and airframe components made of aluminum alloys in the aerospace industry.
2. Resistance Seam Welding

Resistance seam welding is one of the most common welding processes used to join metal sheets with a continuous weld.
In the welding process, two similar or dissimilar materials are joined at the seam. The seam is heated and the heat is from electrical resistance. The weld is performed by roller electrodes instead of tipped electrodes used in spot welding.
In the seam welding process, the welding current is the main parameter.
Seam welding is typically used for making lap joints, tanks that needs pressure-tight or leak-proof, vessels, and also pipes or tubes.
3. Resistance Projection Welding
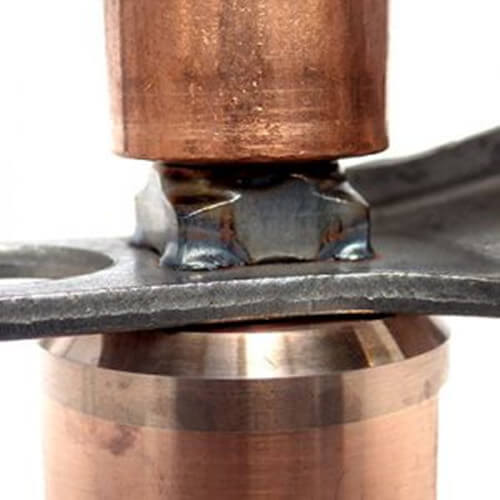

Projection Welding is a form of resistance welding which uses pressure and electrical current to join two or more metal parts. The parts have one or more specific points with the maximum amount of contact.
This process is similar to spot welding but with more weld strength. It can be used for steel sheet connection and also weld nut, threaded stud, or projection to an assembly.
4. Resistance Butt Welding

In resistance welding processes, butt welding can be called the simplest and most versatile one. When two pieces of metal are placed end-to-end and there is no overlap between them, this process welds along the joint.
After getting to know the resistance welding, we are going to introduce types of resistance welding electrodes for you.
When starting with resistance welding, electrode material choices are an important lesson. Electrode materials include Copper, Tungsten, and Molybdenum; They can also be alloys like tungsten copper, tungsten alloy, WLa, WT, MoLa, and TZM. Besides the material, Electrode size and also shape are also key factors for a successful weld.
RWMA COPPER ALLOYS
RWMA 1 Copper (Copper, Zirconium)
Material: The CDA No. is C15000. It is a zirconium copper alloy with heat treatment.
It is recommended to be used as a welding electrode for it has a better performance than pure copper.
Application: It is always used as electrodes for spot welding and seam welding. And it can be used for welding aluminum alloys, brass and bronzes, coated materials, and magnesium alloys.
RWMA Class 2 (Copper, Chromium)
Material: The CDA No. is C18200. Its composition is a Chromium Copper alloy with heat treatment and cold work. It has a high conductivity.
Application: It is always used as electrodes for spot welding and seam welding of clean mild steel, low alloy steels, stainless steel, low conductivity brasses and bronzes, nickel-silver, nickel, nickel alloys, and monel. It is also used as structural parts for almost all types of resistance welding.
RWMA Class 2 (Copper, Chromium, Zirconium)
Material: The CDA No. is C18150. Its composition is a chromium-zirconium copper alloy with heat treatment. It has minimum electrical and hardness specifications of Class 2 material. Under high operating temperature, it has good creep resistance.
Application: It is always used as electrodes for welding galvanized steel and other metallic-coated materials.
RWMA Class 3 (Copper, Nickel, Berylium Free)
Material: The CDA No. is C18150. Its composition is a chromium-zirconium copper alloy with heat treatment. It has minimum electrical and hardness specifications of Class 2 material. Under high operating temperature, it has good creep resistance.
Application: It is always used as electrodes for welding galvanized steel and other metallic-coated materials.
RWMA Class 10 (Copper Tungsten)
Material: Class 10 has two types. One (1W3) has a composition of 45% copper and 55% tungsten. And the other (5W3) has a composition of 30% copper and 70% tungsten. This grade has perfect wear resistance and strength. Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity are also good.
Application: It is always used as electrode inserts for flash and butt welding. The material can also be used as a faced electrode for spot welding low conductivity ferrous metals.
RWMA Class 11 (Copper Tungsten)
Material: Class 11 (10W3) has a composition of 25% copper and 75% tungsten. This grade has perfect wear resistance and strength and thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity are also good.
Application: It is always used as flash-welding and butt-welding electrode inserts, especially when good electrical and thermal conductivity is necessary. The material can also be used for projection welding. For most nut and stud welding, the electrode uses RWMA class 11 as the electrode face. It is also used for light electrical upsetting, electro forging dies, and seam welder bushing inserts.
RWMA Class 12 (Copper Tungsten)
Material: Class 12 (30W3) has a composition of 20% copper and 80% tungsten. This grade has perfect wear resistance and strength and thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity are also good.
Application: It is always used as heavy-duty projection welding electrodes and electro-forming and electro-forging electrodes facings for upsetting studs and rivets. In cross wire welding of large diameter wire and rod, RWMA Class 12 is often used.
RWMA Class 13 (Pure Tungsten)
Material: Class 13 has a composition of pure tungsten and tungsten purity is above 99.95%. Tungsten is a very hard material and hard to machine. But in resistance welding, it can endure high temperatures and be wear-resistant.
Application: It can be used as an electrode by itself or it needs to be joined by the copper shaft. Pure tungsten is used in cross wire welding of copper and brass, resistance brazing, and some upsetting, welding of braided copper wire to other materials.
RWMA Class 14 (Pure Molybdenum)
Material: Class 14 has a composition of pure molybdenum and moly purity is above 99.95%. Molybdenum is a rather softer material compared with tungsten. It also has good thermal conductivity with a high melting point and low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Application: It can be used as an electrode by itself or it needs to be joined by the copper shaft. Pure tungsten is used in cross wire welding of copper and brass, resistance brazing, and some upsetting, welding of braided copper wire to other materials.
Welding Electrodes made of tungsten, molybdenum, and their alloys are more suitable for welding highly conductive materials such as copper.
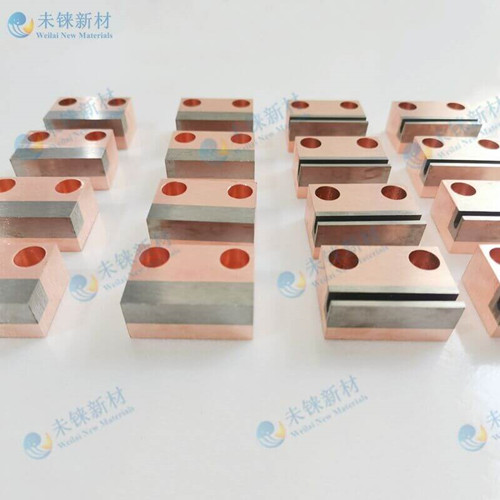
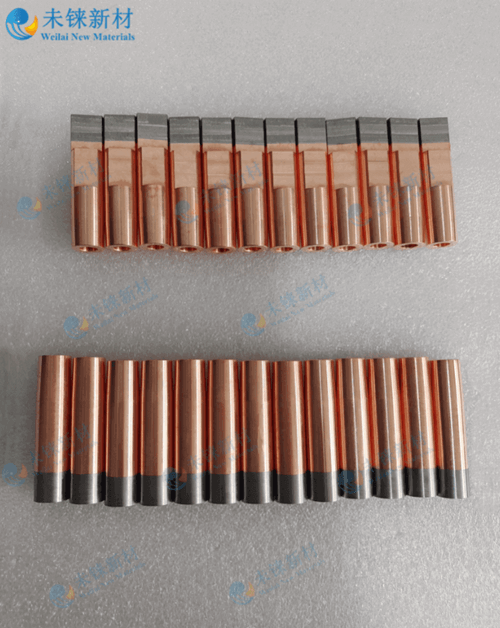
We are a professional producer of rods, plates, cubes, and disks made from tungsten, molybdenum, tungsten copper, and tungsten alloy. And we also produce resistance welding electrodes related to refractory metals.


Address:
No.103, Building 2, Tiantai Jingu Industry Park,
Tian Yuan District,Zhuzhou, Hunan, China.